
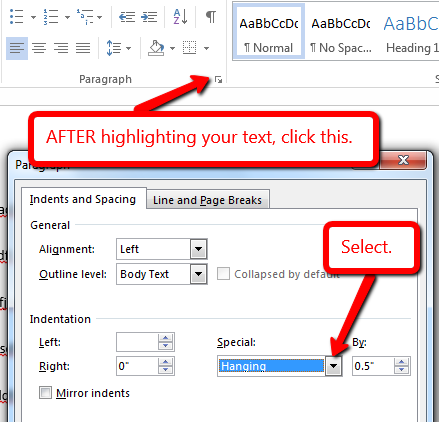
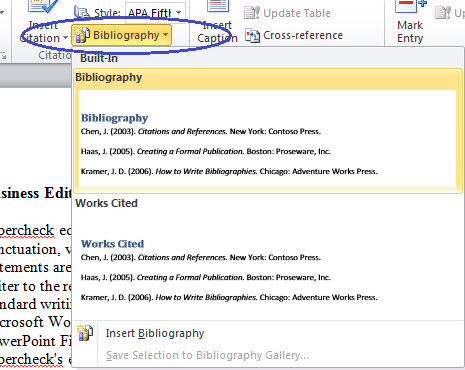
* Reference management software / Citation creatorīibliography - Bib li*og ra*phy (bb l*g r*f) n. * Webliography - websites (the first use of the word "webliography" recorded in the Oxford English Dictionary dates from June 1995) Specialised bibliographies of non-book materials include: Textual bibliography is another name for textual criticism. Descriptive bibliography is the close examination of a book as a physical object, recording its size, format, binding, and so on, while historical bibliography takes a broader view of the context in which a book is produced, in particular, printing, publishing and bookselling. The critical study of bibliography can be subdivided into descriptive (or physical), historical, and textual bibliography. However, the catalogs of some national libraries effectively serve as national bibliographies, as the national libraries own almost all their countries' publications. These descriptions, usually a few sentences long, provide a summary of the source and describe its relevance.īibliographies differ from library catalogs by including only relevant items rather than all items present in a particular library. Annotated bibliographies give descriptions about how each source is useful to an author in constructing a paper or argument. One particular instance of this is the list of sources used or considered in preparing a work, sometimes called a "reference list".Ĭitation formats vary, but an entry for a book in a bibliography usually contains the following information:Īn entry for a journal or periodical article usually contains:Ī bibliography may be arranged by author, topic, or some other scheme. Ī bibliography is a list, either indicative or comprehensive, of writings sharing a common factor: this may be a topic, a language, a period, or some other theme.
The 17th century then saw the emergence of the modern meaning, that of description of books. In the 12th century, the word started being used for "the intellectual activity of composing books". The word "bibliographia" (βιβλιογραφία) was used by Greek writers in the first three centuries AD to mean the copying of books by hand. Now, both categories of bibliography cover works in other formats including recordings, motion pictures and videos, graphic objects, databases, CD-ROMs and websites. Institut d'histoire du livre, 2004.] In earlier times, bibliography mostly focussed on books. Excerpted from Jean Peters, ed., "Book Collecting: A Modern Guide" (New York and London: R. " Bibliographical Society of America, 2003. Bibliographical works are almost always considered to be tertiary sources.īibliographic works differ in the amount of detail depending on the purpose, and can be generally divided into two categories: enumerative bibliography (also called compilative, reference or systematic), which results in an overview of publications in a particular category, and analytical, or critical, bibliography, which studies the production of books. A library catalog, while not referred to as a "bibliography", is bibliographic in nature. As separate works, they may be in bound volumes such as those shown on the right, or computerised bibliographic databases. Bibliographies range from "works cited" lists at the end of books and articles to complete, independent publications. On the whole, bibliography is not concerned with the literary content of books, but rather the "bookness" of books.Ī bibliography, the product of the practice of bibliography, is a systematic list of books and other works such as journal articles. βιβλιογραφία, "bibliographia", literally "book writing"), as a practice, is the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects in this sense, it is also known as bibliology (from Greek _gr.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
